Authenticate with Azure DevOps
If you use the dbt Cloud IDE or dbt Cloud CLI to collaborate on your team's Azure DevOps dbt repo, you need to link your dbt Cloud profile to Azure DevOps, which provides an extra layer of authentication.
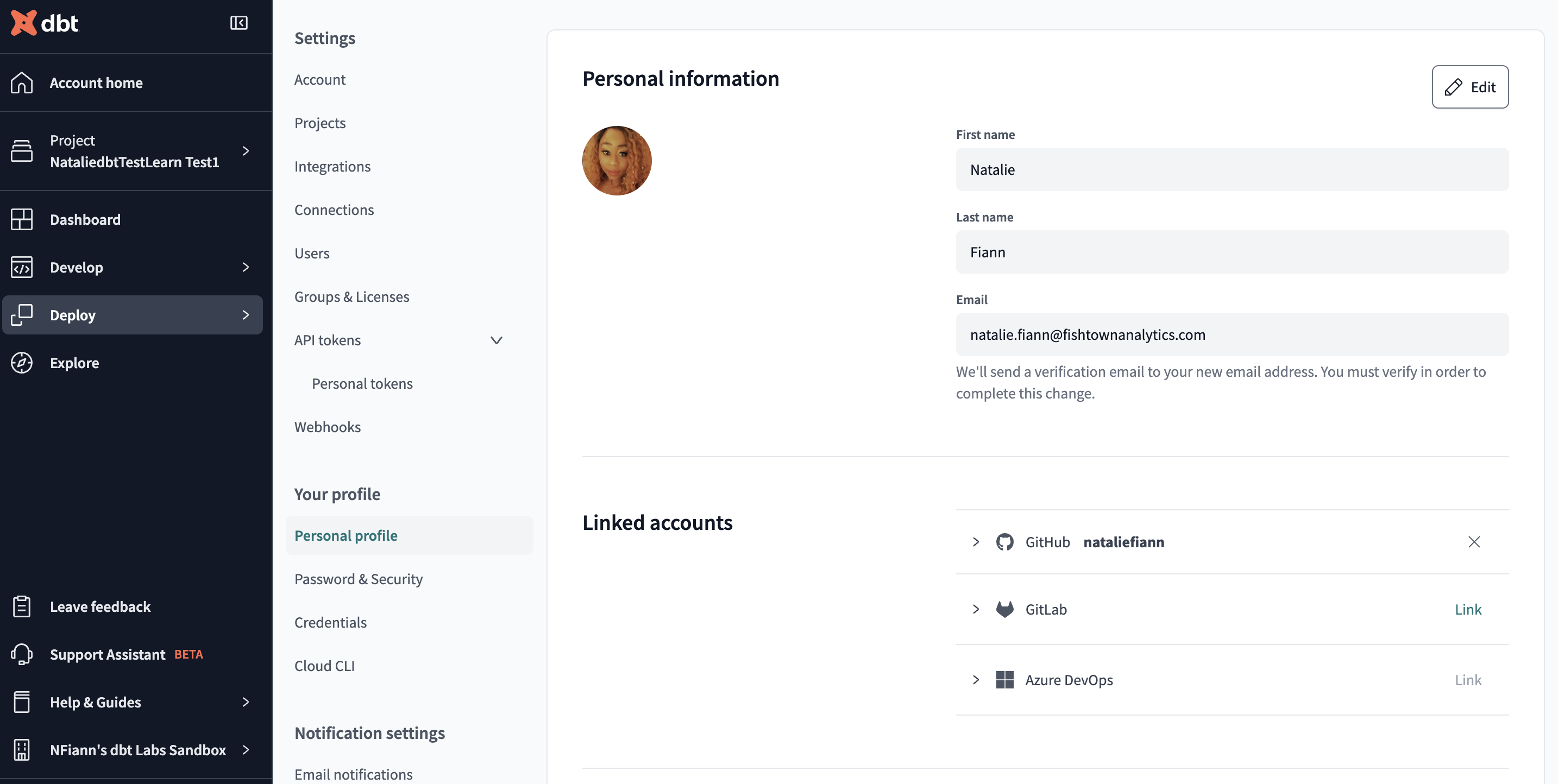
Link your dbt Cloud profile to Azure DevOps
Connect your dbt Cloud profile to Azure DevOps using OAuth:
-
Click your account name at the bottom of the left-side menu and click Account settings
-
Scroll down to Your profile and select Personal profile.
-
Go to the Linked accounts section in the middle of the page.
-
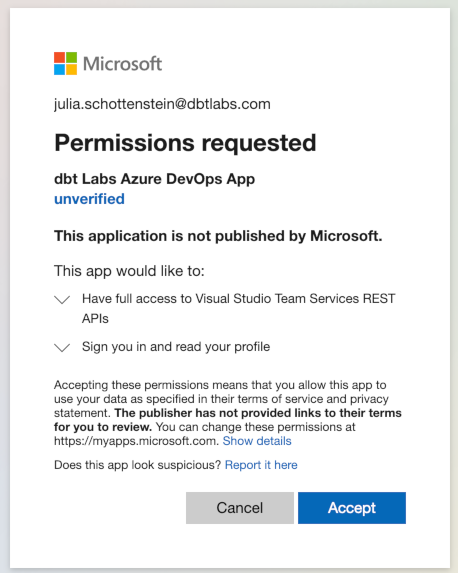
Once you're redirected to Azure DevOps, sign into your account.
-
When you see the permission request screen from Azure DevOps App, click Accept.
You will be directed back to dbt Cloud, and your profile should be linked. You are now ready to develop in dbt Cloud!
FAQs
A .gitignore file specifies which files git should intentionally ignore or 'untrack'. dbt Cloud indicates untracked files in the project file explorer pane by putting the file or folder name in italics.
If you encounter issues like problems reverting changes, checking out or creating a new branch, or not being prompted to open a pull request after a commit in the dbt Cloud IDE — this usually indicates a problem with the .gitignore file. The file may be missing or lacks the required entries for dbt Cloud to work correctly.
Fix in the dbt Cloud IDE
To resolve issues with your gitignore file, adding the correct entries won't automatically remove (or 'untrack') files or folders that have already been tracked by git. The updated gitignore will only prevent new files or folders from being tracked. So you'll need to first fix the gitignore file, then perform some additional git operations to untrack any incorrect files or folders.
- Launch the Cloud IDE into the project that is being fixed, by selecting Develop on the menu bar.
- In your File Explorer, check to see if a
.gitignorefile exists at the root of your dbt project folder. If it doesn't exist, create a new file. - Open the new or existing
gitignorefile, and add the following:
# ✅ Correct
target/
dbt_packages/
logs/
# legacy -- renamed to dbt_packages in dbt v1
dbt_modules/
- Note — You can place these lines anywhere in the file, as long as they're on separate lines. The lines shown are wildcards that will include all nested files and folders. Avoid adding a trailing
'*'to the lines, such astarget/*.
For more info on gitignore syntax, refer to the Git docs.
- Save the changes but don't commit.
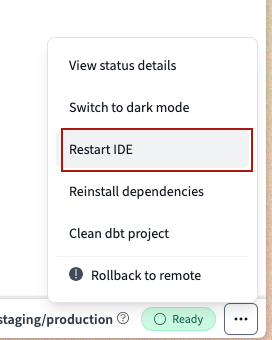
- Restart the IDE by clicking on the three dots next to the IDE Status button on the lower right corner of the IDE screen and select Restart IDE.
-
Once the IDE restarts, go to the File Explorer to delete the following files or folders (if they exist). No data will be lost:
target,dbt_modules,dbt_packages,logs
-
Save and then Commit and sync the changes.
-
Restart the IDE again using the same procedure as step 5.
-
Once the IDE restarts, use the Create a pull request (PR) button under the Version Control menu to start the process of integrating the changes.
-
When the git provider's website opens to a page with the new PR, follow the necessary steps to complete and merge the PR into the main branch of that repository.
- Note — The 'main' branch might also be called 'master', 'dev', 'qa', 'prod', or something else depending on the organizational naming conventions. The goal is to merge these changes into the root branch that all other development branches are created from.
-
Return to the dbt Cloud IDE and use the Change Branch button, to switch to the main branch of the project.
-
Once the branch has changed, click the Pull from remote button to pull in all the changes.
-
Verify the changes by making sure the files/folders in the
.gitignorefile are in italics.
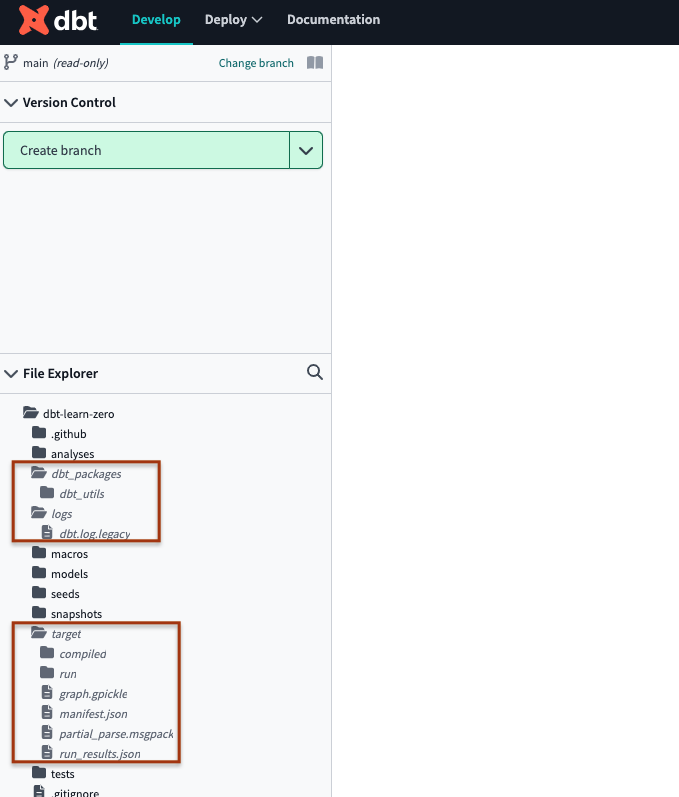 A dbt project on the main branch that has properly configured gitignore folders (highlighted in italics).
A dbt project on the main branch that has properly configured gitignore folders (highlighted in italics).Fix in the git provider
Sometimes it's necessary to use the git providers web interface to fix a broken .gitignore file. Although the specific steps may vary across providers, the general process remains the same.
There are two options for this approach: editing the main branch directly if allowed, or creating a pull request to implement the changes if required:
- Edit in main branch
- Unable to edit main branch
When permissions allow it, it's possible to edit the .gitignore directly on the main branch of your repo. Here are the following steps:
- Go to your repository's web interface.
- Switch to the main branch and the root directory of your dbt project.
- Find the
.gitignorefile. Create a blank one if it doesn't exist. - Edit the file in the web interface, adding the following entries:
target/
dbt_packages/
logs/
# legacy -- renamed to dbt_packages in dbt v1
dbt_modules/
- Commit (save) the file.
- Delete the following folders from the dbt project root, if they exist. No data or code will be lost:
target,dbt_modules,dbt_packages,logs
- Commit (save) the deletions to the main branch.
- Switch to the dbt Cloud IDE, and open the project that you're fixing.
- Rollback your repo to remote in the IDE by clicking on the three dots next to the IDE Status button on the lower right corner of the IDE screen, then select Rollback to remote.
- Note — Rollback to remote resets your repo back to an earlier clone from your remote. Any saved but uncommitted changes will be lost, so make sure you copy any modified code that you want to keep in a temporary location outside of dbt Cloud.
- Once you rollback to remote, open the
.gitignorefile in the branch you're working in. If the new changes aren't included, you'll need to merge the latest commits from the main branch into your working branch. - Go to the File Explorer to verify the
.gitignorefile contains the correct entries and make sure the untracked files/folders in the .gitignore file are in italics. - Great job 🎉! You've configured the
.gitignorecorrectly and can continue with your development!
If you can't edit the .gitignore directly on the main branch of your repo, follow these steps:
- Go to your repository's web interface.
- Switch to an existing development branch, or create a new branch just for these changes (This is often faster and cleaner).
- Find the
.gitignorefile. Create a blank one if it doesn't exist. - Edit the file in the web interface, adding the following entries:
target/
dbt_packages/
logs/
# legacy -- renamed to dbt_packages in dbt v1
dbt_modules/
- Commit (save) the file.
- Delete the following folders from the dbt project root, if they exist. No data or code will be lost:
target,dbt_modules,dbt_packages,logs
- Commit (save) the deleted folders.
- Open a merge request using the git provider web interface. The merge request should attempt to merge the changes into the 'main' branch that all development branches are created from.
- Follow the necessary procedures to get the branch approved and merged into the 'main' branch. You can delete the branch after the merge is complete.
- Once the merge is complete, go back to the dbt Cloud IDE, and open the project that you're fixing.
- Rollback your repo to remote in the IDE by clicking on the three dots next to the IDE Status button on the lower right corner of the IDE screen, then select Rollback to remote.
- Note — Rollback to remote resets your repo back to an earlier clone from your remote. Any saved but uncommitted changes will be lost, so make sure you copy any modified code that you want to keep in a temporary location outside of dbt Cloud.
- Once you rollback to remote, open the
.gitignorefile in the branch you're working in. If the new changes aren't included, you'll need to merge the latest commits from the main branch into your working branch. - Go to the File Explorer to verify the
.gitignorefile contains the correct entries and make sure the untracked files/folders in the .gitignore file are in italics. - Great job 🎉! You've configured the
.gitignorecorrectly and can continue with your development!
For more info, refer to this detailed video for additional guidance.
To migrate from one git provider to another, refer to the following steps to avoid minimal disruption:
-
Outside of dbt Cloud, you'll need to import your existing repository into your new provider.
As an example, if you're migrating from GitHub to Azure DevOps, you'll need to import your existing repository (GitHub) into your new git provider (Azure DevOps). For detailed steps on how to do this, refer to your git provider's documentation (Such as GitHub, GitLab, Azure DevOps)
-
Go back to dbt Cloud and set up your integration for the new git provider, if needed.
-
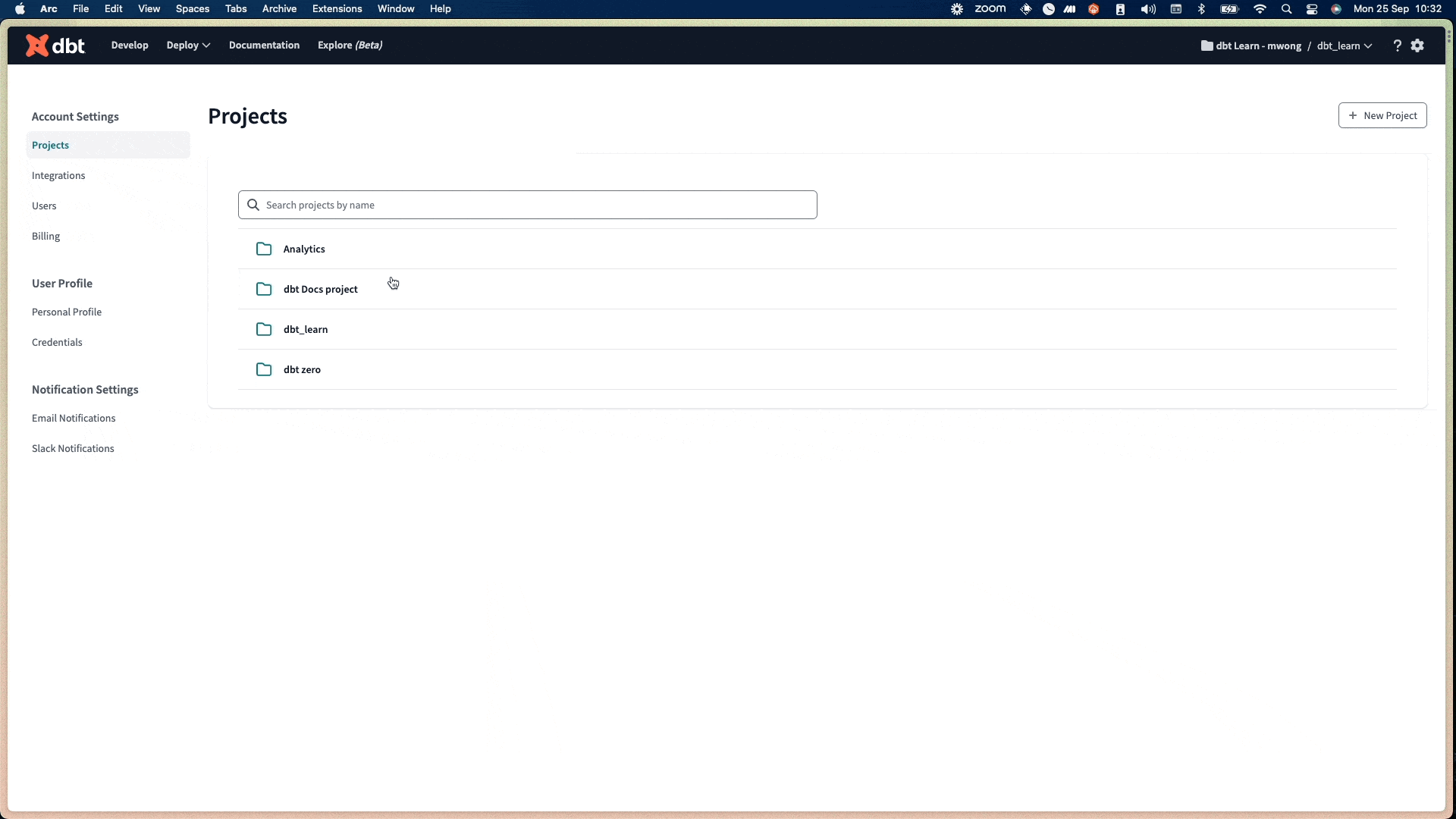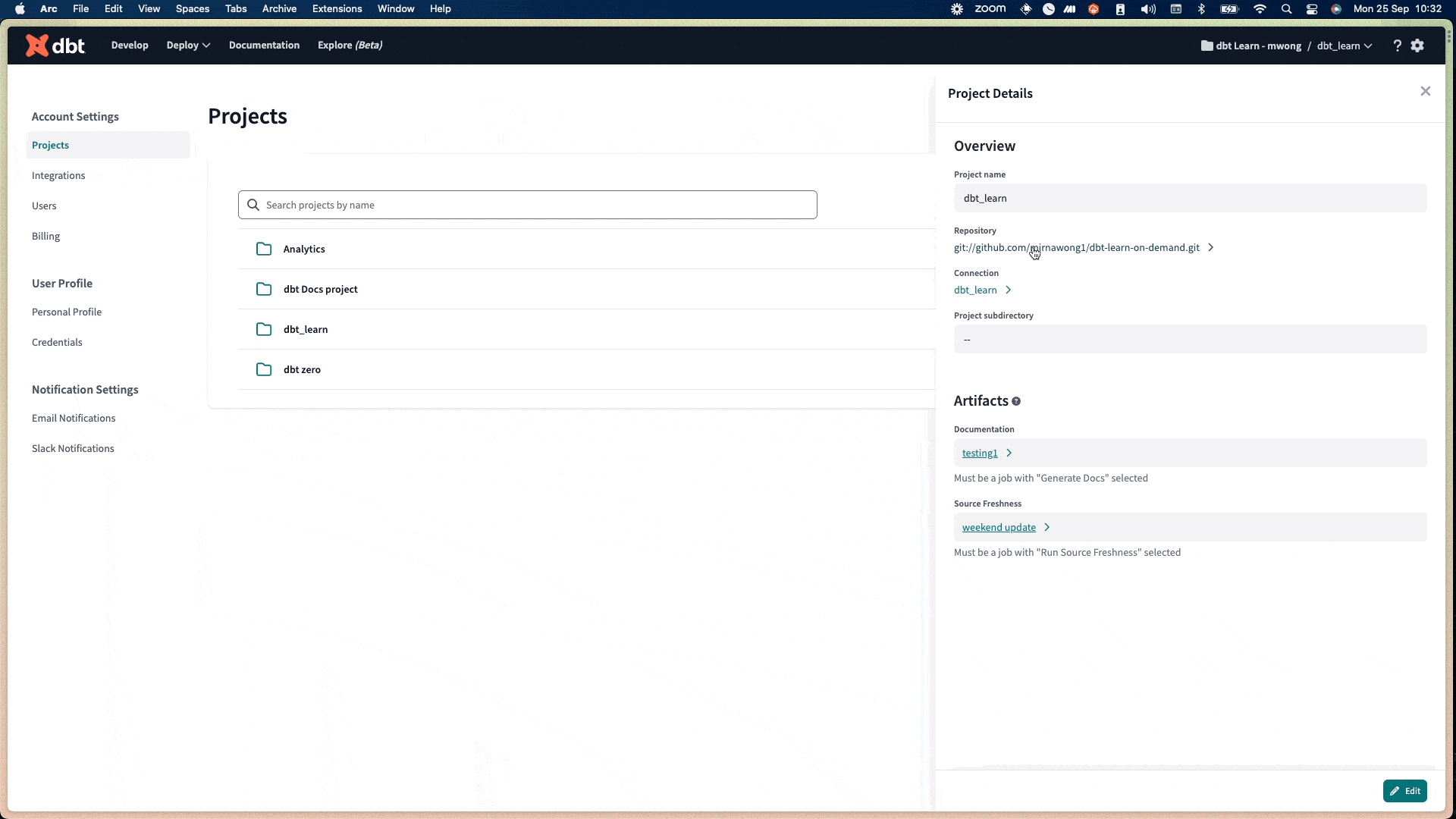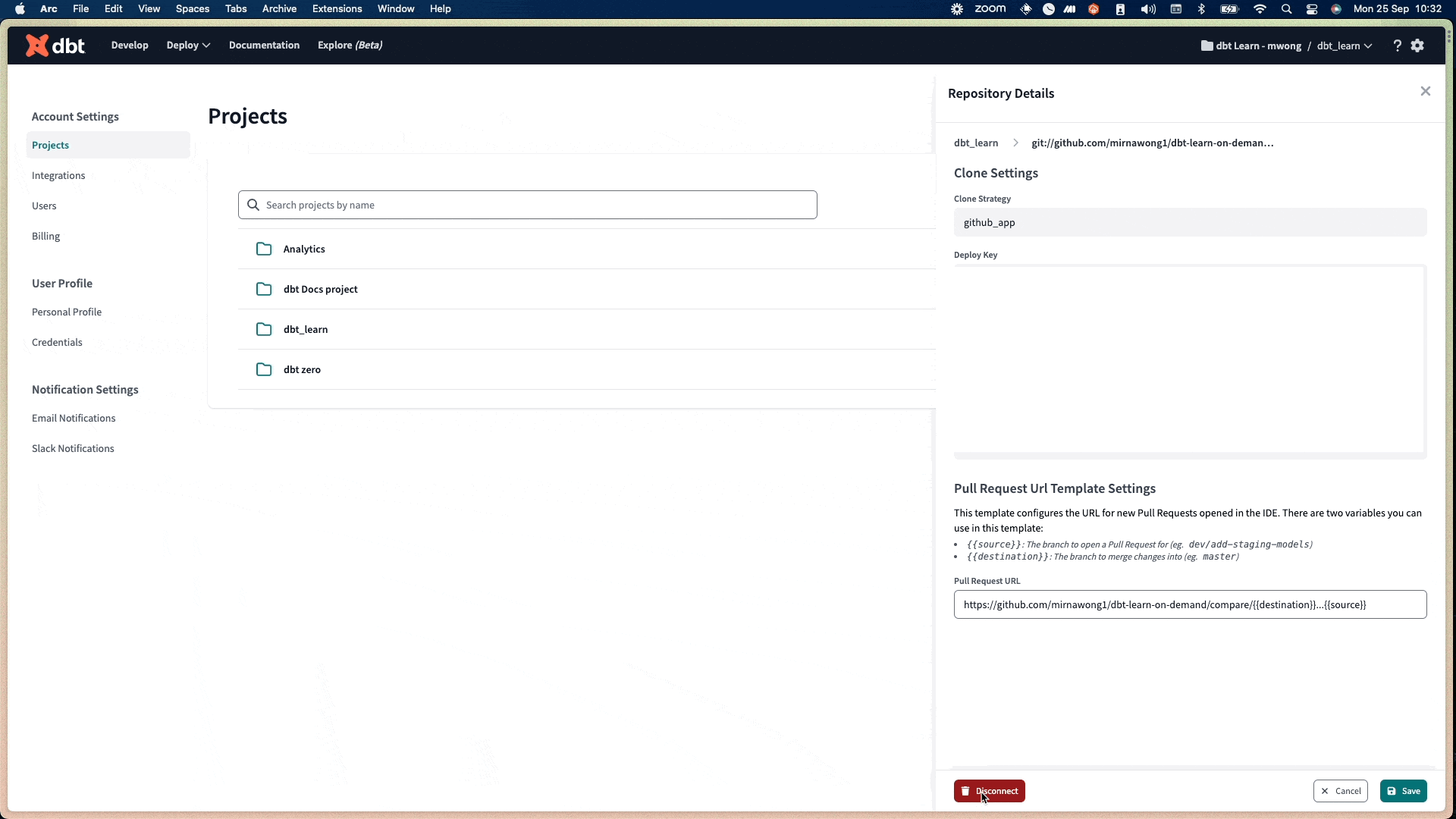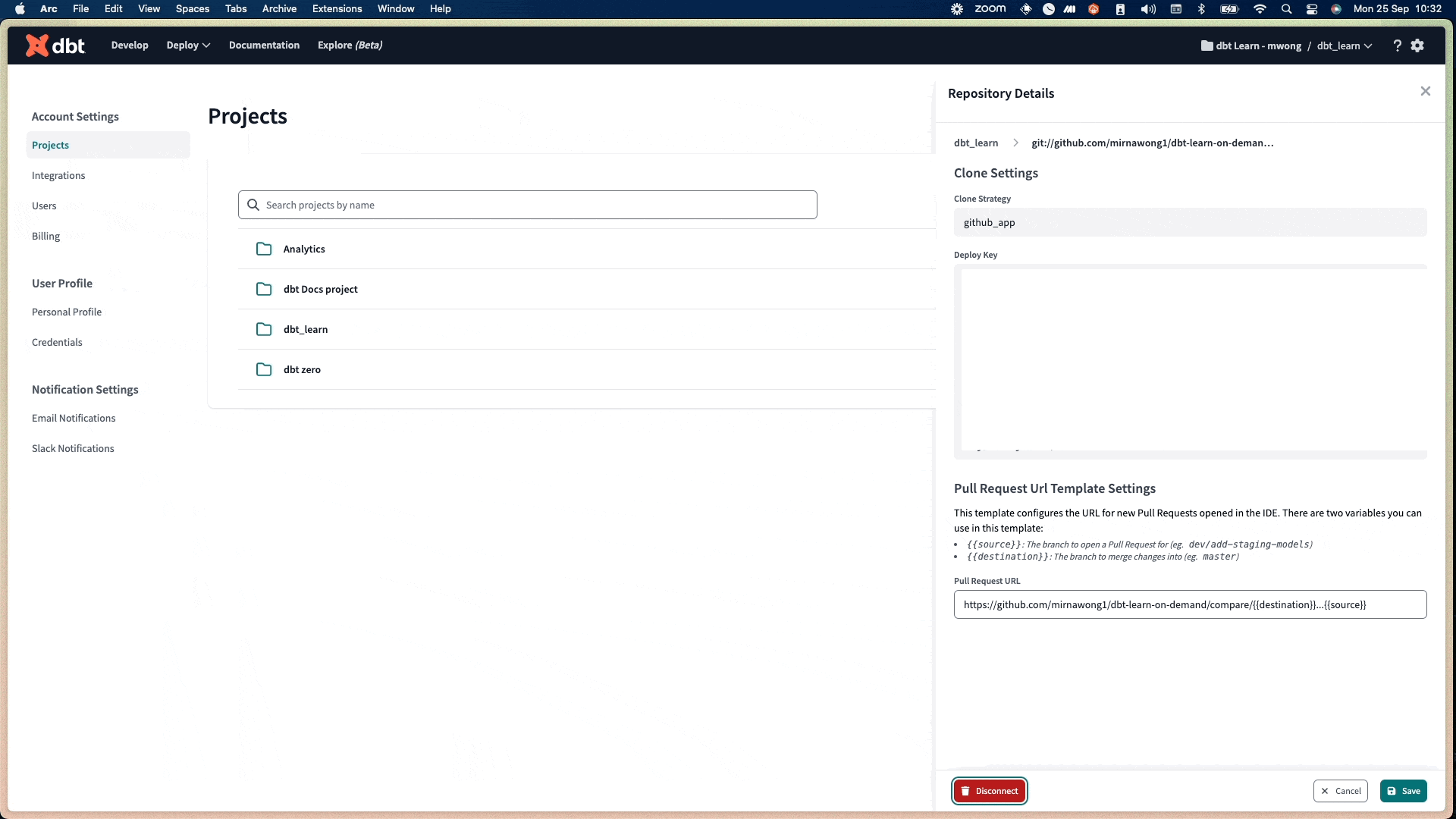
Disconnect the old repository in dbt Cloud by going to Account Settings and then Projects. Click on the Repository link, then click Edit and Disconnect.
-
On the same page, connect to the new git provider repository by clicking Configure Repository
- If you're using the native integration, you may need to OAuth to it.
-
That's it, you should now be connected to the new git provider! 🎉
Note — As a tip, we recommend you refresh your page and dbt Cloud IDE before performing any actions.